Friday, 7.03pm
Sheffield, U.K.
I personally think there’s going to be a greater demand in 10 years for liberal arts majors than there were for programming majors and maybe even engineering, because when the data is all being spit out for you, options are being spit out for you, you need a different perspective in order to have a different view of the data. – Mark Cuban
I was reading a paper by Chris Huxham and Siv Vangen titled “Researching organizational practice through action research: Case studies and design choices”, and came across the phrase “deliberate and systematic data collection is essential, whether it be data such as flip chart notes made at a meeting…”
This stuck with me because I hadn’t thought of notes on a flip chart or whiteboard as “data”, but I suppose it is, everything is – when it’s collected. We tend to assume that data is a particular thing, like numbers or statistics, but it is actually everything. What we find unnerving about Google and Facebook is that they collect it all, whatever we do is monitored and stored and then something happens with it later.
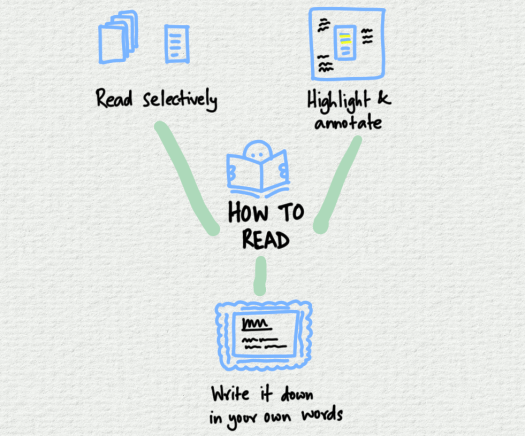
The thing about data, however, is that it is useful to have it, whatever you do. For example, I’ve realised that I have spent most of my life creating data – once I learned to write anyway. I wrote when I was younger because it helped me think and early in my career I learned that taking notes during every meeting was a good habit to get into. There’s no point asking whether something is worth recording or not. Record it first and ask questions later. This has become a twenty-year habit And I hope it continues.
The reason you write, however, is not just to record. It’s so that you have space in your brain to observe and see the total context – the widest possible picture of what is going on. Without notes you’ll remember only a few things. With notes, you can ask more and explore widely. And if you take good notes, visual ones, you can map out understanding very effectively indeed.
But once you have this data what do you do with it? In the collection of essays, “Analyzing qualitative data”, Christina Hughes talks about Schatzman and Strauss’ argument that notes can be Observational Notes (ON), Theoretical Notes (TN) or Methodological Notes (MN). I see this recommendation as one to take notes about what you’re seeing, notes about what you think about what you’re seeing, and notes on how you’re going about making notes and thinking about what you’re seeing.
The reason why you might want to get better at collecting data is that once you have it and develop the skills to understand it life becomes a whole lot easier. If you think of a sales meeting as an exercise in data collection you’ll approach it very differently to if you think of it as an exercise in psychological manipulation. Any meeting, in fact, from one with your child to one with your boss and even one with yourself, will go much more easily if you first seek to collect data and then look to understand and make decisions on the basis of what you’ve collected.
Cheers,
Karthik Suresh