Tuesday, 8.00pm
Sheffield, U.K.
The heart and soul of good writing is research; you should write not what you know but what you can find out about. – Robert J. Sawyer
For those of you reading this for the first time I’m using this blog as a place to practice writing – a way to develop the skills and techniques needed to create long form work. I suppose it would be nice if the work was useful and readable and you liked it – but that’s not the aim of the project – to get you to like something. It’s a practice, an attempt to improve by intentionally working on the art of putting words one after the other and trying to get them to make sense.
I started writing a few years ago and quickly honed in on a formula that seemed to work for me. I’d start with an idea or a model, draw a representation, look for a quote that seemed relevant and then start writing. The first few years were mostly about exploring management theory and looking at models that people had put out there. A random walk down ideas lane. But really it was whatever I was thinking about or what caught my eye. There was no plan other than to sit down every day at around the same time and write something and hit publish.
There was, of course, no real reaction. The Internet wasn’t waiting to read my half-baked thoughts. I pushed things onto social media and I’m sure people who knew me wondered what I was doing but were too polite to say what they thought. And some friends liked stuff which gave me a bit of a boost. But I think I eventually figured out that just because you do something that doesn’t mean it’s worth sharing and shut down all the automatic posts – apart from one lonely Twitter account that has recent content on there.
But what I did start to learn, from that experience, was about the importance of showing up. It’s hard to get started – that first step to overcome inertia is quite often the hardest one you’ll take. But once you get moving it’s a lot easier to keep moving. Once you’ve written for a week it’s easier to know you can do another week. After a year, you know you can do another year. And the days go by, relentlessly, whether you do your thing or not. And now, 977 posts later, I’m pretty confident that, if I sit down and start tapping these keys, another one will pop out.
The second thing I’ve realised is that you’ll see benefits in places you didn’t expect to see them when you start a new habit. Writing for pleasure makes writing for work much easier. When you practice articulating ideas daily then it’s easier to do it under pressure. When you work with models day after day then coming up with one for a client is a simple thing to do. This thing that I do as a practice has had unexpected professional benefits – including helping me deepen my own understanding of Systems Thinking and Practice.
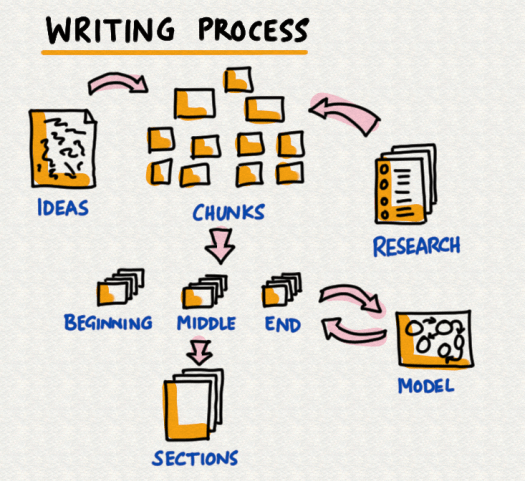
But writing about different things every day does not add up to a useful body of work. To do that, you have to start planning – something I resist doing with every fibre of my being – but I’ve discovered a way that works for me. With some caveats. The general model is shown in the picture above.
I start with an idea, a central theme – perhaps the title of a book. I’m only doing non-fiction at the moment – I don’t feel anywhere near being able to try my hand at storytelling. The first thing to do is get some ideas down on a sheet of paper – a sort of brainstorm that works through things that come to mind. Then I take a bunch of A6 slips of paper and write down an idea or question on each slip – just filling them in as I go along. Some of these slips are also informed by research – from the work I’ve done previously, although I had a problem on my most recent project and we’ll come back to that in a minute. We’ll end up with 30-50 slips of paper at the end of this process.
The next thing to do is sort the big set of slips into ones that seem like they should be in the beginning, middle or end. There’s no sorting within the piles yet – just dropping them into three stacks and one more for unsure. Then I pick up each stack and compare the slips, putting them in what seems like a logical order.
This last step is important to notice because of the mathematical optimisation involved. I can’t really be bothered to check the formulas so trust me on this. If you try and put 30 slips of paper in logical order then you’ll have to go through a lot more comparisons than if you first put those slips in 3 sets of 10 each and then sort the 10 in each set at a time. It’s a lot faster doing it the second way. This is, in fact, a standard team bonding exercise. Give people 15 steps and ask them to discuss them and put them in order. If they try and talk through all of them they’ll never get it done. If they chunk it into a start, middle and end, and then order the 5 steps in each one it will get done pretty quickly.
Okay, so now we have our slips – I then pick up the first one and draw a model – a picture, nodes and arrows – something that can hold the idea. and start writing. And when I’m writing – it’s just writing. I don’t stop and think – the keys sort of press themselves as the words flow through me. I’m just reading what’s appearing on the screen without really trying to make them get there. That’s when it works.
Oh yes.. before I start any writing session, I do three paragraphs of freewriting, just to get things moving before getting on to the actual topic.
So, this makes the writing sound quite easy, and I suppose it is. But that doesn’t mean what I create is any good. And I’ve had two main issues.
The first has to do with research. With my first couple of projects all that random writing over the years was actually research – many of the things I had read and written about resurfaced in the points and arguments I was making. By the third project, however, I had started to run out of material and that lack of research made it much harder to get a flow going. I didn’t know what I was talking about – I was trying to think through it and write about it at the same time. And that’s not easy. The research feeds you and if you stop reading and start watching TV instead you’ll find that you’ll start to run out of ideas.
The second thing had to do with editing. I wrote my first two projects in sentences rather than paragraphs – you know that blog habit where you press enter after every sentence because that’s what you do. Well, don’t do that. It’s a nightmare to edit because you have to collect your sentences together again. It’s the maths problem with the slips of paper again except this time you’re working with 18,000 lines rather than 50 slips. So that was a bad idea.
But in my most recent project I’ve managed to improve the paragraphing but failed on the research. And I don’t know what’s worse – well, anything that increases effort is worse so I’m going to have to say when you do your first draft do your research and write in paragraphs.
That seems obvious, doesn’t it? But it’s taken me 205,642 words to work that out. That’s ok though – I’m a slow learner. Give me time.
What else then… oh yes, word count. The number of words I come out with goes up and down but in a normal session an easy number is around 600-800. It takes some effort to put past a thousand. In 2020, with lockdown, I averaged 1,019 words per post but I think that was pushing it beyond the point that was sensible. It’s like driving in the red so this year I’m easing back down to the 800s. Not this post – it’s gone way beyond – but in principle anyway.
Okay – so I’ve tried to write three books and had different kinds of issues with each one. Do I try and fix them or do I throw that stuff away and move to the next one? Or do I spend 2021 doing some research. That’s probably the way things are going to go. I’m planning on starting a research programme so perhaps what I read is what I write about over the next 12 months.
Perhaps that’s the thing to look at in the next post.
Cheers,
Karthik Suresh